Within the early 2020s, quantum computing hit the general public highlight as a possible risk to Bitcoin. Counting on SHA-256 cryptographic hash operate for its proof-of-work community consensus, Bitcoin’s worth relies on computational energy.
If there’s a know-how that may circumvent the normal binary system of 0s and 1s for models of data, there may be potential to upend cryptography as we all know it. However is that hazard over exaggerated?
Might quantum computing at some point flip Bitcoin right into a worthless piece of code? Let’s begin by understanding why Bitcoin depends on cryptography.
Bitcoin’s Bits and Hashing
After we say that a picture is 1 MB in measurement, we are saying that it accommodates 1,000,000 Bytes. As every Byte accommodates 8 bits, which means a picture accommodates 8,388,608 bits. Because the binary digit (bit), that is the tiniest unit of data, both 0 or 1, that builds up the whole edifice of our digital age.
Within the case of a picture, bits in a 1MB file would assign a colour to every pixel, making it readable to the human eye. Within the case of a cryptographic operate like SHA-256 (Safe Hash Algorithm 256-bit), developed by the NSA, it might produce 256 bits (32 Bytes) because the fastened size of a hash from an enter of arbitrary measurement.
The first goal of a hash operate is to transform any string of letters or numbers into an output of fastened size. This obfuscation mixing makes it superb for compact storage and anonymized signatures. And since the hashing course of is a one-way road, hashed information is successfully irreversible.
Due to this fact, once we say that SHA-256 supplies a 256-bit safety, we imply to say that there are 2256 potential hashes to think about for reversal. When Bitcoin funds are performed, every Bitcoin block has its personal distinctive transaction hash generated by SHA-256. Every transaction inside the block contributes to this distinctive hash as they type the Merkle root, plus the timestamp, nonce worth and different metadata.
A would-be blockchain attacker must recalculate hashes and extract the necessary data not just for that block containing the transactions, however for all subsequent blocks chained to it. Suffice to say, the 2256 risk load poses a nearly impractical computational endeavor, requiring immense expenditure of vitality and time, each of that are exceedingly expensive.
However may this now not be the case with quantum computing?
New Quantum Paradigm for Computing
Shifting away from bits as 0s and 1s, quantum computing introduces qubits. Leveraging the noticed property of superposition, these models of data can’t solely be both 0 or 1 however each concurrently. In different phrases, we’re shifting away from deterministic computing to indeterministic computing.
As a result of qubits can exist in an entangled and superimposed state, till noticed, computations grow to be probabilistic. And since there are extra states than at all times 0 or 1, a quantum pc has the flexibility for parallel computing as it may well concurrently course of 2n states.
A basic binary pc must run a operate for every potential 2n state, which the quantum pc may assess concurrently. In 1994, mathematician Peter Shor developed an algorithm with this in thoughts.
Shor’s algorithm combines Quantum Fourier Remodel (QFT) and Quantum Section Estimation (QPE) strategies to speedup pattern-finding and theoretically break all cryptography techniques, not simply Bitcoin.
Nevertheless, there may be one big downside. If quantum computing is probabilistic, how dependable is it?
Stabilizing Coherence in Quantum Computing
When it’s stated that qubits are superimposed, that is akin to visualizing a coin flip. Whereas within the air, one can think about the coin having each states – heads or tails. However as soon as it lands, the state is resolved into one consequence.
Equally so, when qubits are resolved, their state collapses into the classical state. The issue is {that a} ground-breaking algorithm like Shor’s wants many qubits to keep up their superposition for a protracted time frame to work together with one another. In any other case, the required, helpful calculations fail to really full.
In quantum computing, this refers to quantum decoherence (QD) and quantum error correction (QEC). Furthermore, these issues should be solved throughout many qubits for advanced calculations.
In response to the Millisecond Coherence in a Superconducting Qubit paper printed in June 2023, the longest coherence time of a qubit is 1.48 ms at common gate constancy of 99.991%. The latter share refers back to the total reliability of a QPU (quantum processing unit).
At current, probably the most usable and highly effective quantum pc seems to be from IBM, dubbed Quantum System Two. A modular system prepared for scaling, Quantum System Two ought to carry out 5,000 operations with three Heron QPUs in a single circuit by the tip of 2024. By the tip of 2033, this could improve to 100 million operations.
The query is, would this be sufficient to materialize Shar’s algorithm and break Bitcoin?
QC Risk Viability
As a consequence of decoherence issues and fault-tolerance, quantum computer systems have but to pose a severe threat to cryptography. It’s unclear whether it is even potential to realize a fault-tolerant quantum system at scale when such a excessive degree of environmental purity is required.
This contains electron-phonon scattering, photon emissions and even electron to electron interactivity. Furthermore, the higher the variety of qubits, that are obligatory for Shor’s algorithm, the higher the decoherence.
But, though these could look like intractable issues inherent with quantum computing, there was nice progress in QEC strategies. Living proof, Riverlane’s Deltaflow 2 technique performs real-time QEC on as much as 250 qubits. By 2026, this technique ought to outcome within the first viable quantum software with million real-time quantum operations (MegaQuOp).
To interrupt SHA-256 inside at some point, 13 million qubits could be wanted, based on the AVS Quantum Science article printed in January 2022. Though this could threaten Bitcoin wallets, many extra qubits, at round 1 billion, could be wanted to really execute a 51% attack on Bitcoin mainnet.
In the case of implementing the Grover algorithm, designed to leverage QC to look unstructured databases (distinctive hashes), a research paper printed in 2018 instructed that no quantum pc would be capable of implement it till 2028.
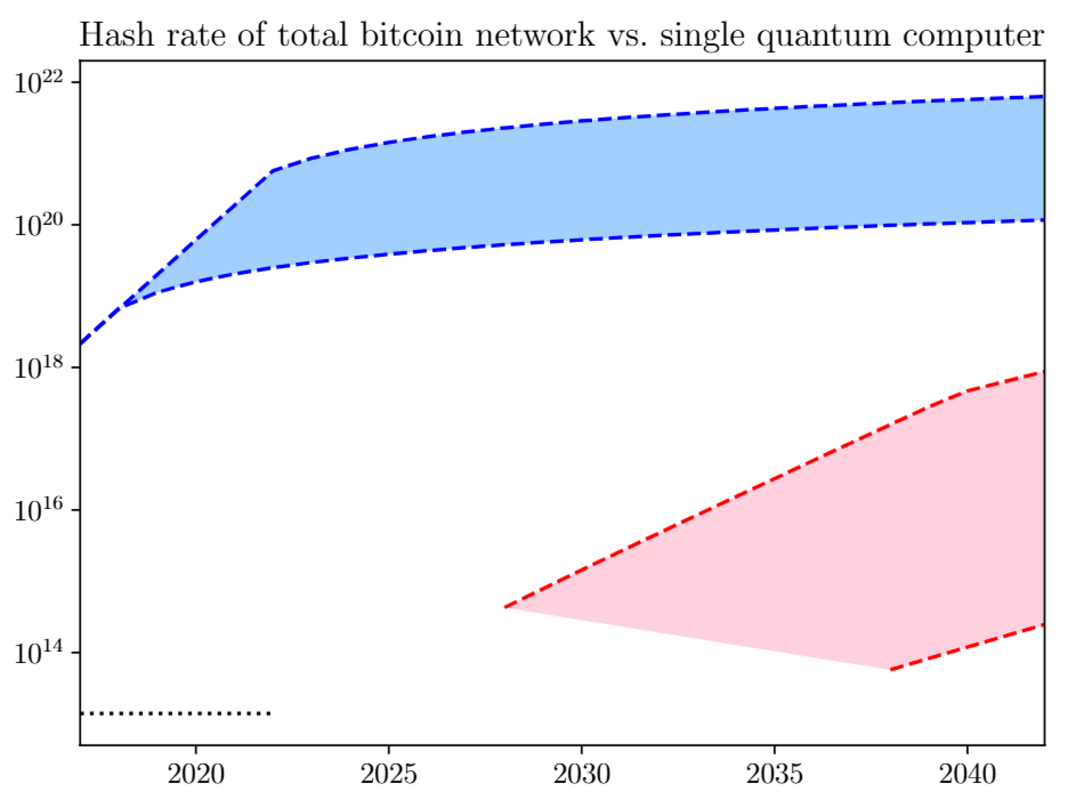
Picture credit score: Ledger Journal
After all, Bitcoin community’s hashrate has vastly elevated since then, and QC has to deal with decoherence as a serious impediment. But when QEC roadmaps ultimately materialize into dependable quantum techniques, what might be achieved to counteract the QC risk to Bitcoin?
Quantum Computing Resistance
There are a number of proposals to safeguard Bitcoin holders from quantum computer systems. As a result of a 51% QC assault is extraordinarily inconceivable, the main focus is especially on hardening wallets. In spite of everything, if individuals can not depend on their BTC holdings to be safe, this could trigger an exodus from Bitcoin.
In flip, BTC worth would plummet and the community’s hashrate would drastically lower, making it much more weak to QC than beforehand estimated. One such hardening is implementing Lamport signatures.
With Lamport signatures, a personal key could be generated into pairs, 512 bitstrings from a 256-bit output. A public key could be generated with a cryptographic operate to every of the 512 bitstrings. Every BTC transaction would wish a one-time Lamport signature.
As a result of Lamport signatures don’t depend on elliptic curves over finite fields in Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA), which is utilized by Bitcoin and might be exploited by Shar’s algorithm, however on hash capabilities, this makes them a viable quantum-resistant various.
The draw back of Lamport signatures is their elevated measurement, upward of 16KB, and one-time use. After all, simply by shifting addresses and preserving BTC in chilly storage, thus avoiding personal key publicity, also can stop QC from being efficient.
One other strategy to confound potential QC assaults could be to implement lattice-based cryptography (LBC). Not like in ECDSA, LBC avoids finite patterns by counting on discrete factors in n-dimensional lattice (grid) area that extends infinitely in all instructions. Due to this function, there has but been developed a quantum algorithm that might break LBC.
Nevertheless, to implement a brand new sort of cryptography, Bitcoin must endure a tough fork. In that state of affairs, there would probably should be many alerts indicating that main breakthroughs in quantum computing, significantly in qubit rely and fault tolerance, are imminent.
Backside Line
It’s protected to say that the Bitcoin mainnet itself will not be at risk from quantum computing, in both the close to or distant future. But, if QC have been to compromise Bitcoin’s encryption—rendering SHA-256 and ECDSA out of date—it might deeply affect confidence within the cryptocurrency.
This confidence is essential, as demonstrated by main corporations like Microsoft and PayPal, which have adopted Bitcoin funds, drawn by as much as 80% savings compared to card transactions, zero chargebacks, and full management over funds. With over 300 million holders globally, Bitcoin’s enchantment as each a safe asset and a cheap fee choice stays sturdy.
Finally, Bitcoin’s worth is sustained by the capital and confidence behind it. Its historical volatility reveals how occasions—starting from Elon Musk’s tweets and PayPal’s integration to ETF launches and the FTX collapse—have impacted market sentiment. A basic risk to Bitcoin’s encryption may result in panicked sell-offs, miner withdrawals, and a decreased mining problem, doubtlessly opening the door to a 51% QC assault with fewer qubits.
To stop such a state of affairs, Bitcoin holders and builders would do nicely to maintain up with QC developments.
It is a visitor publish by Shane Neagle. Opinions expressed are solely their very own and don’t essentially mirror these of BTC Inc or Bitcoin Journal.
















